How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects more than one billion people worldwide and is a leading cause of heart disease and stroke. For decades, researchers have observed that premenopausal women are less likely to develop high blood pressure than men or postmenopausal women. Researchers have known for years that estrogen is the deciding factor, but exactly how it offers this protection has remained unclear.
Rainfall shapes bird populations
Scientists have long focused on rising temperatures to understand how climate change is reshaping the natural world. But there's a critical blind spot in that picture: rain. A new global study reveals precipitation has been largely overlooked in studies of how climate change impacts birds, even though it can be just as influential as temperature.
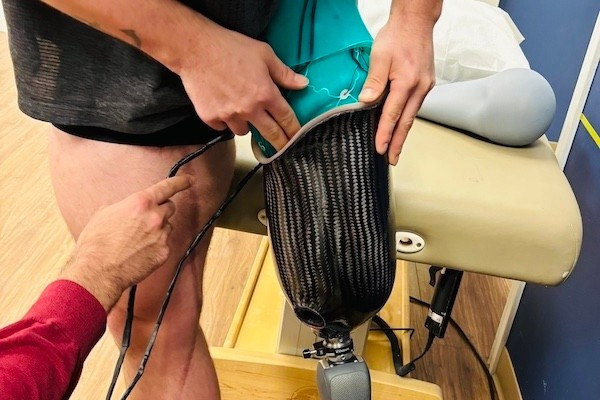
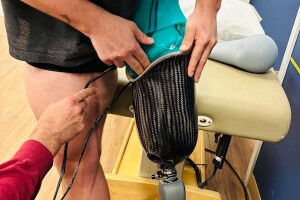
Researchers break the mould with new prosthetic design
A new, fully customizable 3D printed socket design is set to transform the prosthetics industry.
More than eco-anxiety: SFU study exposes emotional fallout of climate crisis for youth
A few years ago, researcher Maya Gislason's young child came home from school with her crayon drawing of the Earth in 2020 and 2050. "The first was blue and green; the second was a planet on fire," she says.
The new ’forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Simon Fraser researchers have uncovered concerning fibreglass contamination in a key estuary on Vancouver Island, raising concerns about how an as-yet overlooked contaminant could affect aquatic birds, marine life and coastal communities that rely on shellfish and seafood.
Tree cover shapes freshwater ecosystems over millennia
In-person class cancellation and work-from-home / Annulation des cours en présentiel et télétravail.
Video games and young people’s mental health: families and schools can make a difference
Researchers say we need to look at the impact of video games on daily life, not just screen time. According to a new study, pre-adolescents who have difficulty managing their video game habits are more likely to experience psychotic-type episodes.
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Neuroscience review demonstrates that connecting with nature shifts brain activity linked to attention and relaxation, helping explain why time outdoors feels restorative Spending time in nature, even
Making solar power’s land use more efficient
Two McGill-led studies suggest rooftop panels and smarter planning increase the clean-energy transition's sustainability. As solar energy rapidly is becoming the world's largest renewable power source, new research from McGill University offers a clearer picture of how much land that growth could require and how smarter choices could mitigate solar energy's land footprint.
Categories
Last News









New DNA tools outperform traditional methods for detecting genetic risk in wildlife

What should AI do and for whom? Graduate College hosts AI and ethics conference
The art of the pitch: UCalgary's Postdoc Research Slam showcases the power of research translation

Women often need stronger professional networks to climb corporate ladder, Western analysis shows

SFU professor to advance equity in seafood supply chains with Pew Fellowship in Marine Conservation